
In today’s fast-paced logistics and warehousing industry, forklifts play a vital role, and the power source of electric forklifts has become a key decision factor.
Battery technology is a core element that directly affects efficiency, operating costs, and productivity. Among the available options, lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries are the two main power solutions, each offering distinct characteristics and advantages in different applications.
Differences Between Lead-Acid and Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries have long been among the most common battery types. Their technology dates back to the mid-1800s.
Lead-acid forklift batteries, also known as "wet-cell batteries," are relatively inexpensive.
Lead-acid batteries generate electricity through an electrochemical reaction between lead plates and a mixture of 30%–50% sulfuric acid and distilled water, known as the "electrolyte solution."
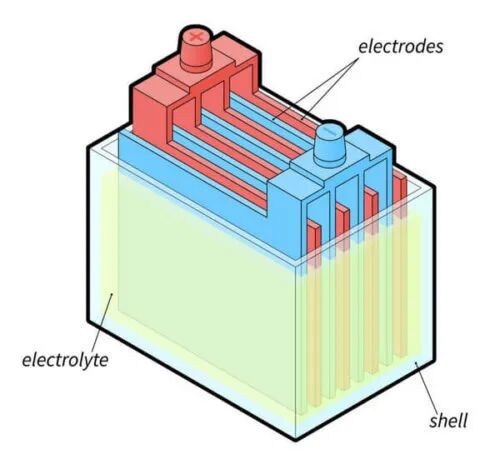
Components of a lead-acid battery include:
- Cells
- Bars
- Plates of lead dioxide
- Cables
- Electrolyte
To produce electricity, an electrochemical reaction occurs between the lead plates and the electrolyte solution. Electric ions flow from the sulfuric acid to the negative plates, generating electricity.
Lead-acid batteries require longer charging times compared to lithium-ion batteries. Charging is primarily done through conventional methods, typically after a shift, using a low current for about 8 to 10 hours until 100% charged.
After prolonged charging, the battery needs to cool for 6 to 8 hours before it can be used again.
Conventional charging is mostly done overnight, making it suitable for single-shift operations.
This also means lead-acid batteries are generally not suited for opportunity charging. Doing so can quickly damage the battery, accelerate wear, and reduce its cycle life.
Overall, lead-acid forklift batteries have a relatively short lifespan, typically lasting 3 to 5 years (or 1,000 to 1,500 charging cycles) under normal weekly operation of 40 hours.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Over the past few decades, lithium-ion batteries have become increasingly common in consumer electronics. Today, they are emerging as an increasingly popular power technology for forklifts.
Lithium-ion forklift batteries consist of the following components:
- Cathode
- Electrolyte (lithium-based)
- Anode
- Separator
- Two current collectors (positive and negative)
To generate electrical energy, lithium-ion batteries utilize various chemical compositions, one of the most commonly used in forklifts being lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄).
The anode and cathode store lithium. When a lithium-ion battery discharges, the electrolyte carries positively charged lithium ions from the anode to the cathode through the separator.
When the battery is charged, the electrolyte moves from the cathode to the anode through the separator, transporting the negatively charged lithium ions
Lithium-ion batteries can be conveniently charged through opportunity charging due to their fast-charging capability. This type of charging uses specialized high-current chargers to rapidly recharge the batteries.
Opportunity charging can be performed as needed or when convenient, making lithium-ion batteries more efficient.
With proper maintenance, lithium-ion forklift batteries can last for 2,000 to 3,000 cycles, or approximately 7 to 10 years (based on 300 working days per year).
How to Determine if Lithium-Ion Batteries Are Suitable?
In material handling operations, efficiency and productivity are two critical keys to success.
There are only so many hours in a day. Therefore, gaining a competitive edge often comes down to finding ways to accomplish more work in less time.
Can lithium forklift batteries provide such advantages? Here are key factors to consider:

01 Does your operation run on multiple shifts?
Multi-shift applications—such as manufacturing, 3PL (third-party logistics), food processing, and other 24/7 material handling operations—tend to benefit more from lithium-ion batteries.
For these multi-shift operations, lithium-ion batteries may pay for themselves in as little as 36 months.
For single-shift operations, the return on investment for lithium-ion forklift batteries may take five years or longer.
02 Are there cold/frozen storage environments?
Lead-acid batteries do not perform well in cold or freezing conditions. In low temperatures, their capacity decreases by at least 35%.
Lithium-ion forklift batteries retain capacity much better than lead-acid batteries in cold temperatures and can be charged quickly even in refrigerated or freezer environments.
Thus, operations with forklifts operating in cold or frozen settings can benefit quickly from switching to lithium-ion batteries.
03 Are profit margins tight?
If your profit margins are slim, transitioning to lithium-ion forklift batteries can be advantageous. Why?
When you switch to lithium forklift batteries, you can reduce energy costs, reclaim space, and enhance productivity. These improvements are immediate.
Lithium-ion forklift batteries can be up to 40% more energy-efficient than lead-acid batteries and up to 88% more efficient than diesel-powered options.
While lead-acid forklift batteries may have a lower upfront cost, they come with higher maintenance expenses.
Boosting productivity and lowering energy costs are two key ways lithium-ion forklift batteries help save money.
In summary, both lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries offer distinct advantages for electric forklifts. The optimal choice depends on factors such as your operating environment, usage frequency, charging conditions, and long-term cost considerations.
If you are a medium- to large-sized enterprise operating multiple shifts, lithium-ion forklift batteries could be an excellent choice for your needs.
If you are uncertain which battery solution best suits your electric forklift, our team is here to assist. Please feel free to contact us for professional advice and customized battery solutions tailored to your specific application.