As the name suggests, an internal combustion forklift is one that's powered by an internal combustion engine. They typically use diesel, gasoline, or liquefied natural gas as fuel and play a vital role in logistics, warehousing, and manufacturing. For a forklift to operate smoothly and efficiently, the coordination of various components is essential. Simply put, it's a forklift powered by an internal combustion engine (usually diesel or gasoline). This type of forklift is typically used in situations requiring heavy lifting, such as warehouses, factories, or construction sites. It's like a sturdy "porter," but much faster and more powerful than a real porter.
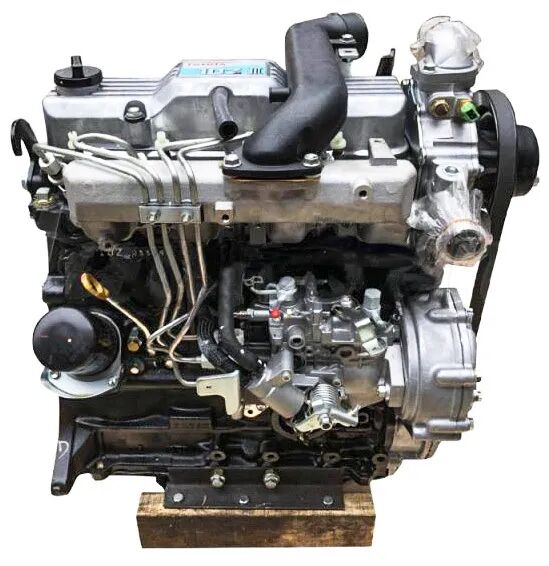
1.Engine: The "Heart" of an IC Forklift
 |
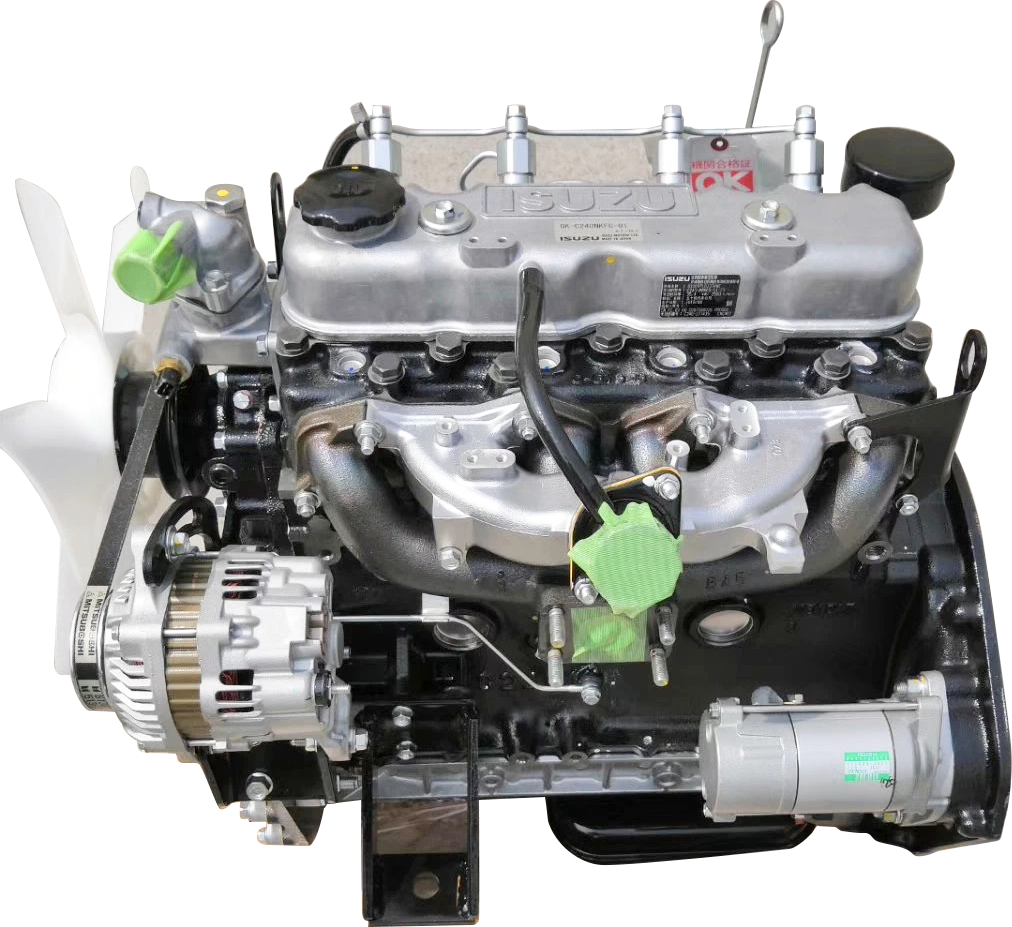 |
The engine of an IC forklift is like its heart, providing the core power for the forklift's operation. The most common types of IC forklift engines include diesel, gasoline, and LPG. Each engine has its own unique characteristics:
Diesel engines: Known for their powerful torque and fuel economy, they are particularly suitable for applications requiring long periods of high loads. Diesel engines are also favored for their increased durability and better fuel efficiency.
Gasoline engines: Generally speaking, gasoline engines are easier to start and are suitable for light-load operations. They may not be as fuel-efficient as diesel engines, but they offer good performance and responsiveness.
LPG engines: These engines offer better environmental performance and lower emissions, making them suitable for environmentally sensitive applications. LPG also burns cleaner, which helps reduce maintenance frequency.
2. Transmission: Converting Power into Action
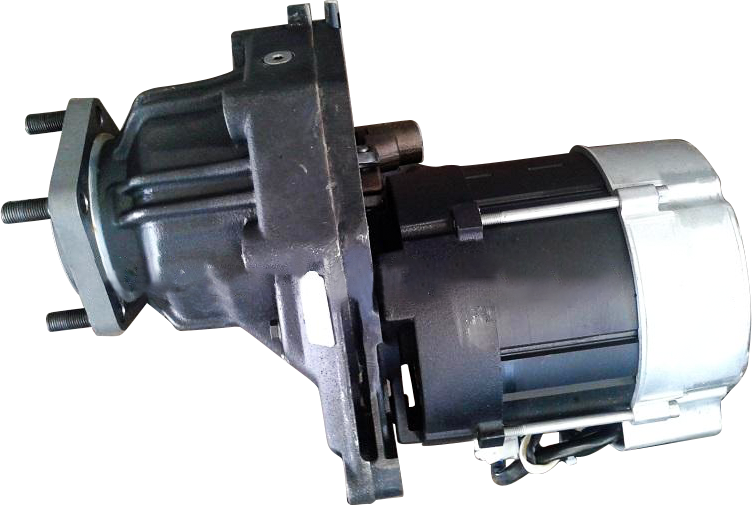
A forklift's transmission system is responsible for converting the engine's power into actual movement. There are two main types of transmission systems:
Manual transmission: This is a more traditional system, requiring the driver to manually operate the gear lever to change the vehicle's speed. While operating it may require some skill, it offers superior controllability.
Automatic transmission: Modern forklifts are increasingly using automatic transmissions, which automatically adjust the vehicle's speed, freeing the driver to focus on other tasks. Automatic transmissions make forklifts easier to operate, making them particularly useful in high-volume operating environments.
3. Fuel System: Maintaining Energy Flow
The fuel system's primary task is to ensure the engine receives sufficient fuel to operate properly. It primarily includes the following components:
Fuel Pump: This pumps fuel from the tank to the engine. Common fuel pumps are mechanical and electric. Mechanical fuel pumps are more common in older forklifts, while modern forklifts mostly use electric fuel pumps, which offer more stable performance.
Fuel Filter: This component removes impurities from the fuel, protecting the engine from damage. Regularly replacing the fuel filter is crucial for maintaining stable forklift operation.
Fuel Tank: The fuel tank's capacity directly affects the forklift's operating time. Ensure the tank is properly sealed to prevent fuel leaks. Regularly check the fuel level to avoid interruptions due to insufficient fuel.
4. Braking System: Safety First
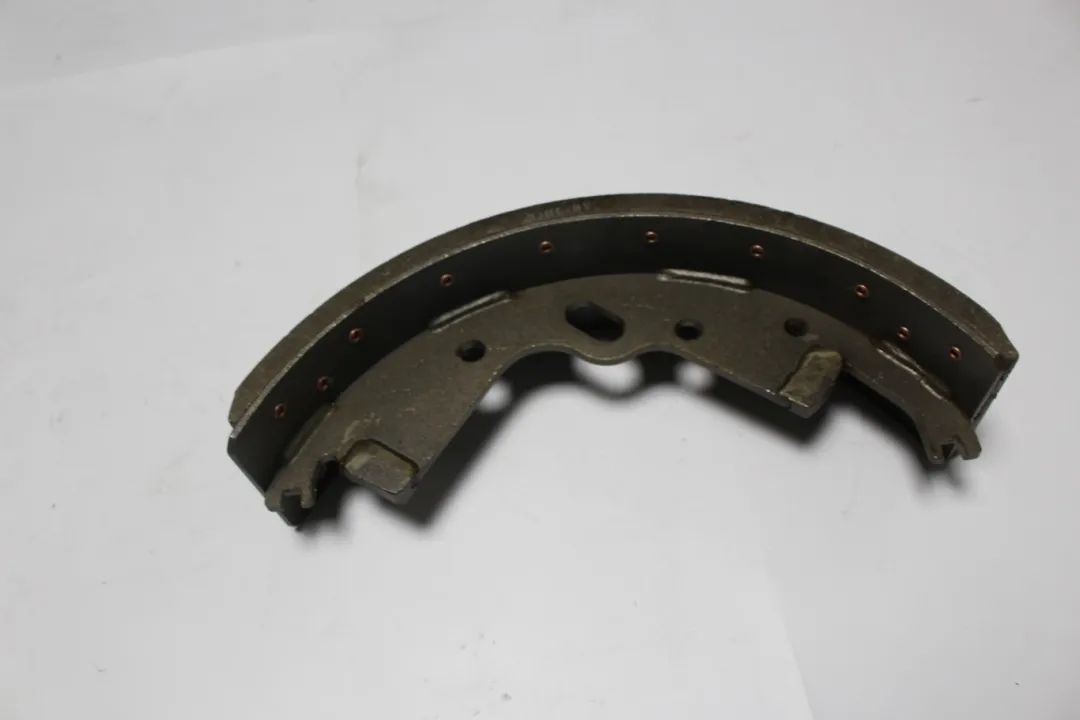

The braking system is a crucial component of forklift safety. Its main components include:
Brake Pads: Brake pads are the most common braking component. With age, they wear out and require regular inspection and replacement.
Brake Fluid: Brake fluid is crucial to the hydraulic braking system, transmitting braking pressure. Regular replacement of brake fluid is essential to ensure the effectiveness of the braking system.
Brake Calipers: Brake calipers clamp the brake discs, producing braking action. Regularly inspecting the working condition of the brake calipers can help prevent potential safety hazards.
5. Tires: Key to Load-Carrying and Stability
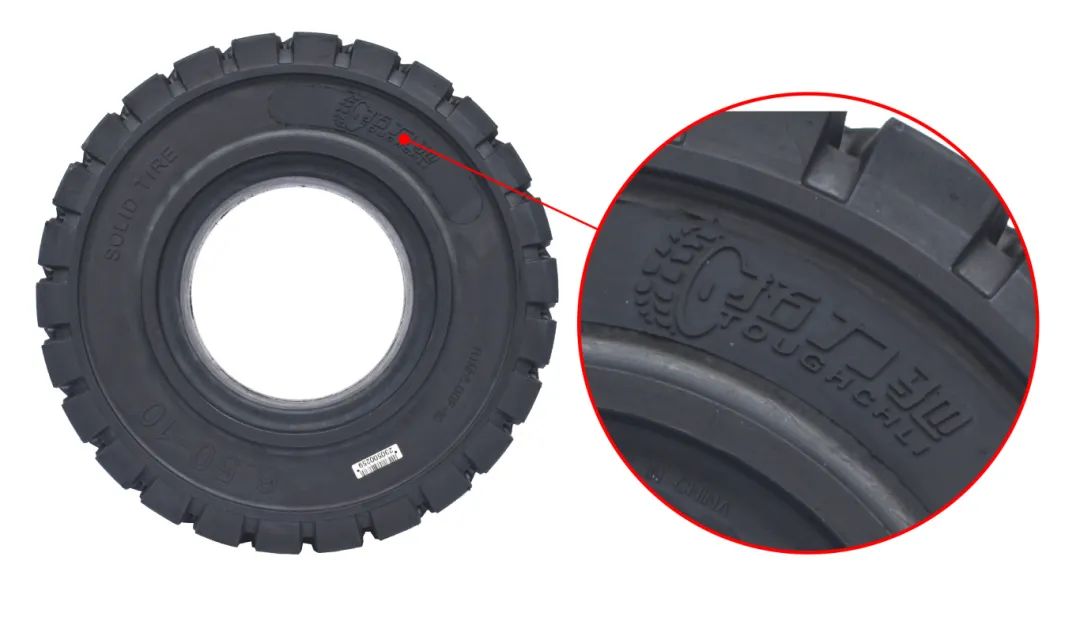

As the only point of contact between a forklift and the ground, tires are of paramount importance. There are two main types of forklift tires:
Solid tires: These tires lack inner tubes and are highly wear-resistant, suitable for use on rough surfaces, offering improved stability and impact resistance.
Pneumatic tires: Pneumatic tires offer improved ride comfort and stability, making them suitable for use on smooth surfaces. However, pneumatic tires require regular tire pressure checks and precautions to avoid punctures from sharp objects.
6. Hydraulic System: A Great Helper for Lifting and Tilt
The hydraulic system is key to a forklift's ability to lift and tilt, and primarily includes:
Hydraulic Pump: This pump delivers hydraulic oil to the hydraulic cylinder, providing lifting force. The performance of the hydraulic pump directly impacts the forklift's operating efficiency.
Hydraulic Cylinder: This cylinder is the primary component for lifting and tilting the forklift. It converts the hydraulic oil's pressure into mechanical force, pushing the forklift's fork arm up and down.
Hydraulic Oil: Hydraulic oil lubricates and transmits pressure within the hydraulic system. Maintaining cleanliness and proper quantity of hydraulic oil is crucial. Regularly check the hydraulic oil level and condition to ensure proper system operation.
7. Body Structure: Strength and Stability
A forklift's body structure, including the frame, fork arms, and support arms, bears the various pressures and loads generated during operation. The body structure requires regular inspection to ensure it is free of cracks or damage.
Frame: The frame is the main body of the forklift, supporting all accessories and loads. The frame's material and structural design significantly impact the forklift's stability and durability.
Fork arms: The fork arms are the primary operating components of the forklift, responsible for gripping and lifting loads. They require regular inspection to ensure they are free of deformation or wear.
Frame: The frame supports various forklift components, such as the hydraulic cylinder and fork arms. The stability of the frame directly impacts the forklift's operational stability.
The various parts of an internal combustion forklift are like a sophisticated system of gears, each silently contributing to its smooth operation. From the engine to the tires, from the fuel system to the hydraulic system, the proper functioning of every component is crucial to ensuring the efficient and safe operation of the forklift.If you need forklift parts, please contact us!
Understanding the functions and maintenance points of these parts can help us better use and maintain our forklifts, extending their service life and reducing failure rates. Whether you are a forklift operator, maintenance technician, or manager, mastering this knowledge will effectively ensure the efficient operation of your forklift.
I hope that today's sharing will give you a clearer understanding of internal combustion forklift parts, allowing you to become more proficient in future forklift maintenance and operation. Let us work together to ensure that our forklifts perform like new and continue to contribute to our industrial and logistics industries!